draw 3d cube in photoshop
From opening a 3D file to rotating, scaling and moving it, working with meshes, creating textures or fifty-fifty materials, adding lights, and more, this tutorial covers virtually of the secrets of the useful characteristic 3D Tools of Photoshop CS4 Extended. If you have it, why don't you try? I tin assure you that you will discover a brand new world of infinite possibilities.
Before Getting Started
We are living on the golden historic period of 3D technology, we tin see art pieces, architectural models, biological simulations, fantasy creatures, futuristic machines, and well-nigh realistic objects everywhere. Most of those graphics have been through Photoshop, from texture editing to final mock-ups; making information technology a must know tool for anyone interested in 3D design.
Photoshop CS3 Extended allowed users to open their 3D files and edit directly some features like textures and lights, but CS4 takes 3D editing into another level where you can actually work with the 3D file just like almost of the commercial 3D editing software. Even though Photoshop tin't edit the model itself, information technology works absolutely well with textures, materials and lights allowing y'all to even pigment directly over a surface using the Brush Tool. This is a very basic guide but some elemental knowledge of 3D geometry is needed.
Tutorial Details
- Program: Photoshop CS4 Extended
- Difficulty: Basic
- Estimated Completion Fourth dimension: two - iii Hours
Y'all volition need some 3D models to play with, I'm using a gunkhole from telias.free.fr and a costless-to-employ model of a space shuttle that I've downloaded from the NASA website. Feel free to use whatsoever model that you want. Let's get started!
Part I - Creating and Editing 3D Layers
Photoshop handle 3D files through 3D layers, which work just like Smart Objects. Each 3D layer contains a unique 3D scene that can exist created v different ways: from a 3D file, from a layer working every bit a Postcard (Aeroplane), from a layer making it a 3D basic Object, from a grayscale layer and as a Book combining 2 or more layers.
This tutorial volition encompass the get-go four, since Volume based on layers is a little bit different than the others and we will leave it for some other occasion.
New Layer from 3D File
The first way and maybe the most known style to piece of work with a 3D layer in Photoshop is creating a 3D layer from an existing file. For this become to 3D > New Layer from 3D File, so chose a file on your file organization and open it. Photoshop allows you to open .3DS, .DAE, .KMZ, .U3D and .OBJ files. A new Layer with the object's name will appear in the Layers Panel. You lot can add equally many 3D layers as you lot desire.



Working with the Basic 3D Tools
In the Tools Console click on the active 3D Tool (K) then on summit, in the Options Panel, you will see several dissimilar options for you to edit the 3D layer. At whatever time you can go dorsum to the default values past clicking on the tiny House Icon in the Options Panel.
Rotate
The default tool and the beginning 1 in the list is Rotate, Click on the 3D model and Drag up or downwardly to rotate it around its 10 centrality, or side to side to rotate it around its Y axis. A diagonal Drag volition rotate the model on both the X and Y axis. You can control the rotation by setting numerical values in the Orientation fields over the Options Panel, by default all of them are set to 0.



Roll
Drag side to side or up and downward to Whorl the model around its Z axis. You can do the same past using the previous tool, but belongings the Option key on a Mac or the Alt key on the PC. You tin can control the rotation by setting numerical values on the Orientation fields.



Drag
This tool moves the model in the 3D space. Drag side to side to motion the model horizontally, or upwardly or down to move it vertically. Hold the Alt key to move it in the X/Z direction. This tool is very different than the standard Move Tool (V) because this works over a 3D environment meanwhile the Move Tool works just in 2D. Yous can command the position by setting numerical values on the Position fields over the Options Panel all values are set in 0 by default.



Slide
Drag side to side to movement the model horizontally, or upwardly or down to move it closer or farther away from your perspective. You lot can control the position by setting numerical values on the Position fields, which is 0 by default.



Scale
This change the model'south size. Elevate up or downward to scale the model larger or smaller. By setting the Scale values in a numeric format y'all can scale the model over any of its 3 axis, stretching it up or enlarging it. By default the numeric values are set to i.



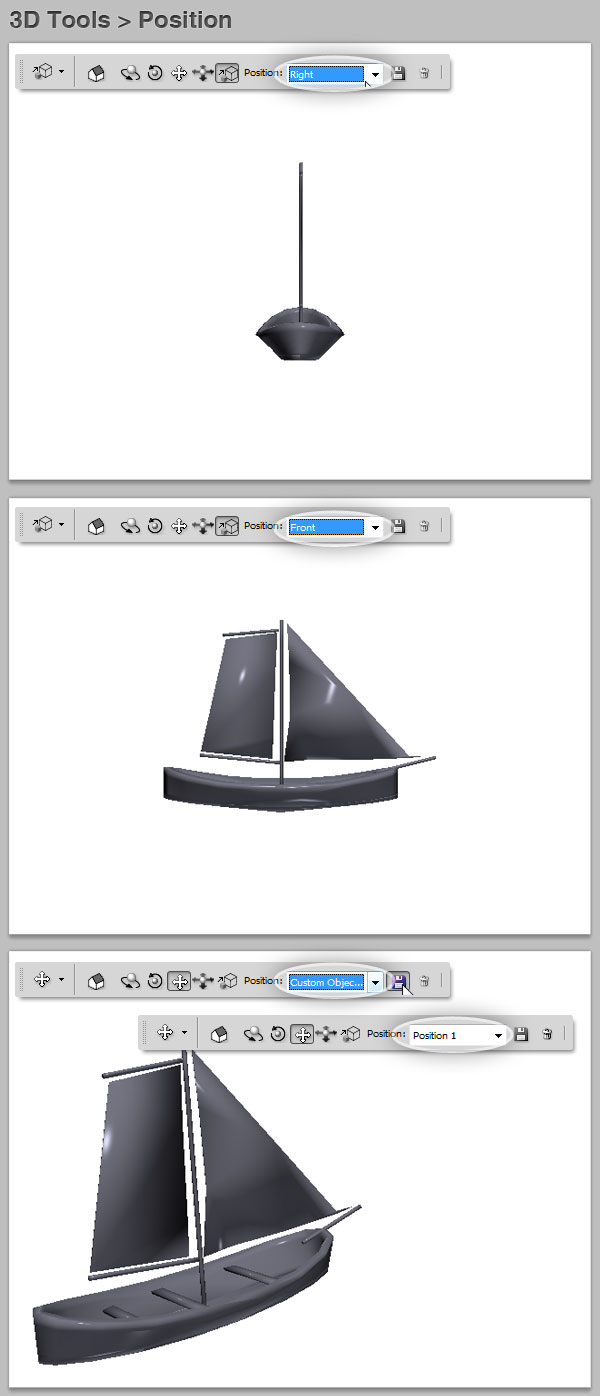
Position Presets
In the Position driblet down you lot will notice several position presets to chose from. Besides you tin can save a customized Position by clicking on the tiny Relieve icon or delete a custom preset from the drop downwards box.


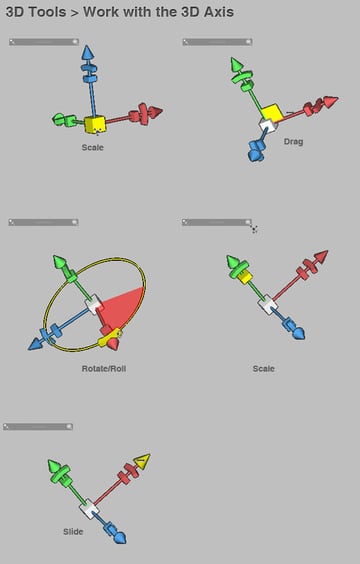
3D Axis
You must take Open GL enabled, go to Edit > Preferences > Performance and in the GPU panel bank check the box named Enable Open up GL Drawing. Then when you create a 3D file, yous'll see a 3D axis handler to work with, information technology does exactly the same every bit the standard 3D tools, just working directly on the axis instead of clicking on the canvas. Beneath at that place's a list of the hotspots of the 3D axis.


Camera
The 3D photographic camera tools are used to movement the camera view, while leaving the position of the 3D object stock-still. This is very useful when you want to merge 3D objects into a single scene (we volition see that soon).
Click on the 3D Camera default tool (N) to activate them. Near of the tools work pretty much the aforementioned as the Position Tools: Rotate, Movement and Drag. You tin switch betwixt Perspective (Vanishing point) and Orthographic (Parallel lines) cameras, and zoom them upward to 180. You can save Photographic camera View Presets as well.



New Shape from Layer
Photoshop allows you to create a agglomeration of built in shapes from 2D layers. Select a Layer in Layers Panel, it can exist any kind of layer, then become to 3D > New Shape From Layer ...There you will find several presets to chose from. As y'all tin can see at the bottom of the image below you can create prissy pieces using just built in shapes.



Postcard from Layer
Another fashion to create a 3D layer is past converting any layer into a 3D Postcard. For this select any layer (vector or bitmap), and then become to 3D > New 3D Postcard from Layer. Then y'all can handle each layer equally a 3D object.



New Mesh from Grayscale
Finally another fashion of creating a 3D layer is from a Grayscale layer. Select any grayscale gradient, shape, or text layer and go to 3D > New Mesh From Grayscale > ... and chose one of the following options: plane, two sided plane, cylinder and sphere. Below in that location's an example of 3D layers based on a gradient layer.



Merge Meshes
You tin can easily merge two or more 3D layers into a single scene. For this y'all need two 3D layers in the same file. In the following example there is a cube and a cylinder. Select i of the layers ("Cube" in this case), then using the Camera Tool ready the View driblet down to the other 3D Layer ("Cylinder"). Finally in the Layers Panel Options Menu go to Merge Down. This way yous volition have a unique 3D layer. Each mesh still tin be edited separately on the 3D Panel.



Part 2 - Working with the 3D Console
Go to Window > 3D to show the 3D Panel. There you will observe several options to accept your models into another level (you must have a 3D layer selected in order to testify all the options on it).
On summit there are four buttons that filter the viewing of the components of the Scene: Scene (All in i), Meshes, Materials and Lights. Below in that location are the Scene objects, first at that place'due south the Scene itself, so a list of all the meshes ,each ane with its respective material, and below a list of the lights. You can toggle the visibility of a mesh, cloth or light anytime you lot want.
Below the Scene explorer there'southward a panel where you tin can change the settings of the selected object (we will dig into this later). Finally, in that location are four footling buttons: Toggle Ground Plane testify/hide a footing plane, Toggle Lights show/hibernate the lights controls, New Calorie-free shows a list of lights to add into the scene, and Delete, which removes the component from the scene.



Scene Render Settings
Anti-Alias
Select the Scene on the object's explorer in the 3D Panel. We will brainstorm with the Anti-Aliasing of the render. In the settings expanse of the 3D Panel there'southward a Drop Down with three anti-aliasing options: Typhoon, Amend and All-time. You can change this setting someday y'all want. Simply retrieve that a better anti-aliasing means more fourth dimension for the system to render the image.



Return Presets
On the Preset drop dow you volition detect a lot of render presets. Below are some examples.



Global Ambient Color
The Global ambient colour is a global colour, which is visible on reflective surfaces (we will see more nigh reflectiveness shortly). By default the global ambient is set to black.



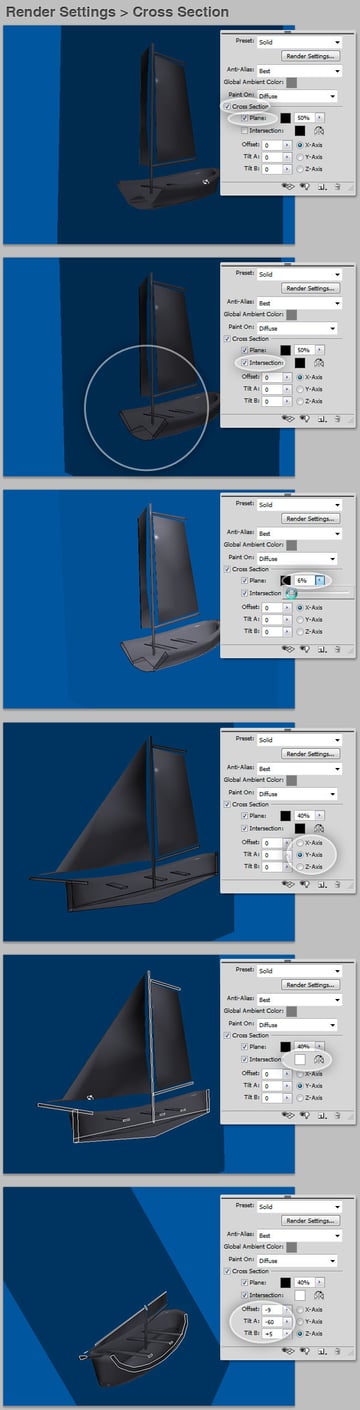
Cross Section
This setting creates a planar cross section that intersects the model trough an axis at the angle y'all choose. It'due south pretty useful in order to see through a model and view interior content. You can alter the color and opacity of the intersecting plane and ascertain a color for the lines. Besides you can change the Offset and Tilt values every bit you wish.


Working with Meshes
Each scene may take several meshes. You lot tin can select them one past one in the peak section of the 3D panel. One time y'all select a mesh the Settings expanse will show a miniature of the Scene and a scarlet rectangle delimiting the mesh. Each mesh tin can exist handled as any 3D object (rotate, whorl, scale, etc.) merely with the tools in the bottom of the 3D Panel, by clicking in the little Abode icon the mesh will go back to its original position and scale.



Office Three - Materials
A fabric is a complex group of texture layers: Diffuse, Bump, Glossiness, Shininess, Opacity, Reflectivity, Surroundings and Normal. Each one with its very own characteristics. Combining them in a proper fashion results in an outstanding or even realistic effect. To edit a material click on the mesh'due south material and see the Settings on the lesser of the 3D Panel.
Diffuse
This texture is the color of the cloth. You tin can either select a colour from the swatch or create a New Texture (or Open an existing i) by clicking on the Texture Map Menu as shown in the tertiary screenshot below.
Once you create a texture layer, it will appear in the Layers Panel. You can Double-click to edit it. A new document with a .PSB extension will be open up there. You can pattern anything y'all want. When you save the document, the 3D layer will be updated.



On the Texture Map Menu there'southward an option named Edit Properties. By clicking on it, you will exist able to chose which layers you want to include in the texture or the entire composite, besides setting the scale and offset of the texture layer. This can be fabricated on every single texture of the material.



Bump
This texture creates bumps in the material's surface. A bump map is a grayscale image in which lighter values create raised surface areas and darker values create flatter surface areas. In the following example there's an irregular grayscale epitome created with a simple Brush and its respective result. The Crash-land Forcefulness field is fix to an corporeality from 1 to 10.
Tip: In lodge to make a texture layer almost perfect, go to Filter > Other > Offset, change both horizontal and vertical beginning and use a clone tool to polish the edges.



Glossiness and Shininess
Glossiness defines the corporeality of light from a source that reflects off the surface and back to the viewer. Shininess defines the dispersion of the reflected light generated by the Glossiness setting. It'south harder to explain than information technology is to effort. Change both values and meet what happens. Don't forget that you lot can add a texture to any of those settings.



Opacity
Increases or decreases the opacity of the material (0-100%). It'due south useful for creating glass textures for case.



Environment and Reflectivity
One of my personal favorites textures on a material is Environment, which stores the image of the environment surrounding the 3D model. In the following example I'yard adding a clouds texture to the Environment option, and voilá, a overnice reflection on the ring'southward surface, you can hide the environment by toggling the eye icon of the Surround texture in the Layers Panel.
Reflectivity here is very of import, since increases the reflection of other objects in the 3D scene, and the environment map, on the material surface. The lower the percentage of reflection the less environment is reflected.



Normal
Another personal favorite, a normal map increases surfaces details. It'southward based on a multi-channel (RGB) image and helps to polish the surface. Below in that location is an example of an orange circumvolve dawn on a normal texture. You tin see the circumvolve zone looks smoother on the 3D model. If the RGB layer covers all the document, then the entire surface will look smoother.
Look at the case below, with a Normal map and a Diffuse texture you can create a nice 3D flag in less than 1 infinitesimal!.



Part IV - Lights
3D lights illuminate models from different angles, adding realistic depth and shadows. You tin add three types of lights in Photoshop: Infinite Lights (like sunlight), Spot Lights like reflectors, and Point lights like bulbs.
Yous can change the position of lights, also colour and intensity. You tin see them at the bottom of the scene explorer, most of models accept at least two Infinite Lights that you can edit, or delete. To create a new layer click on the New Low-cal push button on the lesser of the panel and chose the type of low-cal that y'all want to create.
Space Lights
Once you created or when you're editing a, Space Calorie-free, you lot can customize its Color, Intensity and the ability to Create Shadows. It's pretty useful to toggle the Lite Guides on the bottom of the 3D panel. An Infinite Light tin only be Rotated or by clicking on the tiny Camera icon set up the light on the focal point. You can add together as many Lights as you lot want.



Point Lights
This light works as if y'all are putting a bulb calorie-free somewhere in the model. Yous tin can edit the Position, Intensity, Color, Create Shadows and Softness equally well as Infinite Lights, but you tin Elevate, Move and Rotate this light.



Spot Lights
As well as the other lights, you tin can change the Intensity, Color and Shadows power, move it trough the scene and change the Softness. Too yous can configure the position (in degrees) of the Hotspot and the Falloff.
Finally yous can check Employ Attenuation (how fast light intensity decreases as altitude from objects increases) and modify the Inner and Outer attenuation values. No matter how detailed the screenshot may be, the merely way to see how it works is giving a try.



Office 5 - Some Extras
Paint On
Last just non least the Paint On... Photoshop enables pigment directly over any texture layer of the Materials, Select the Paint On... texture on the 3D console (yous must select the scene first) and from the Tools Console select the Brush tool and customize the settings and colors as you want.
In the following example y'all can encounter how to pigment over the Diffuse Texture using a couple of brushes and even the Eraser Tool. At the bottom of the image below there'south the effect of painting on the Crash-land texture with a soft black brush.



Relieve Materials and Lights Presets
Since creating a material sometimes is a long process, it'southward very applied to create presets of Cloth and Lights to re-use them later. Select a Material, then on the 3D Console's Options Card click on Salve Material/Lights Preset..., type some name for it and salvage it somewhere. To Use a preset on another mesh select Supercede Fabric/Lights...



Decision
This is only a little sample of what can be done with 3D Layers and the advanced 3D Panel, information technology'southward up to you to endeavour these tools and explore its full potential. Good Luck!
Subscribe to the Psdtuts+ RSS Feed for the all-time Photoshop tuts and articles on the web.
Source: https://design.tutsplus.com/tutorials/a-basic-guide-to-photoshops-3d-tools--psd-6042
0 Response to "draw 3d cube in photoshop"
แสดงความคิดเห็น